
Geometric models like DUSt3R have shown great advances in understanding the geometry of a scene from pairs of photos. However, they fail when the inputs are from vastly different viewpoints (e.g., aerial vs. ground) or modalities (e.g., photos vs. abstract drawings) compared to what was observed during training. This paper addresses a challenging version of this problem: predicting correspondences between ground-level photos and floor plans. Current datasets for joint photo-floor plan reasoning are limited, either lacking in varying modalities (VIGOR) or lacking in correspondences (WAFFLE). To address these limitations, we introduce a new dataset, C3, created by first reconstructing a number of scenes in 3D from Internet photo collections via structure-from-motion, then manually registering the reconstructions to floor plans gathered from the Internet, from which we can derive correspondence between images and floor plans. C3 contains 90K paired floor plans and photos across 597 scenes with 153M pixel-level correspondences and 85K camera poses. We find that state-of-the-art correspondence models struggle on this task. By training on our new data, we can improve on the best performing method by 34% in RMSE. However, we also identify open challenges in cross-modal geometric reasoning that our dataset aims to help address.
Our goal is to create a dataset that consists of paired floor plans and photos and annotated correspondences between them. We achieve this through the following steps:
We evaluate a combination of sparse, semi-dense, and dense matching algorithms on our dataset: SuperGlue, LoFTR, DINOv2, DIFT, RoMa, and MASt3R. We also evaluate on DUSt3R. We find that all methods struggle with this task.
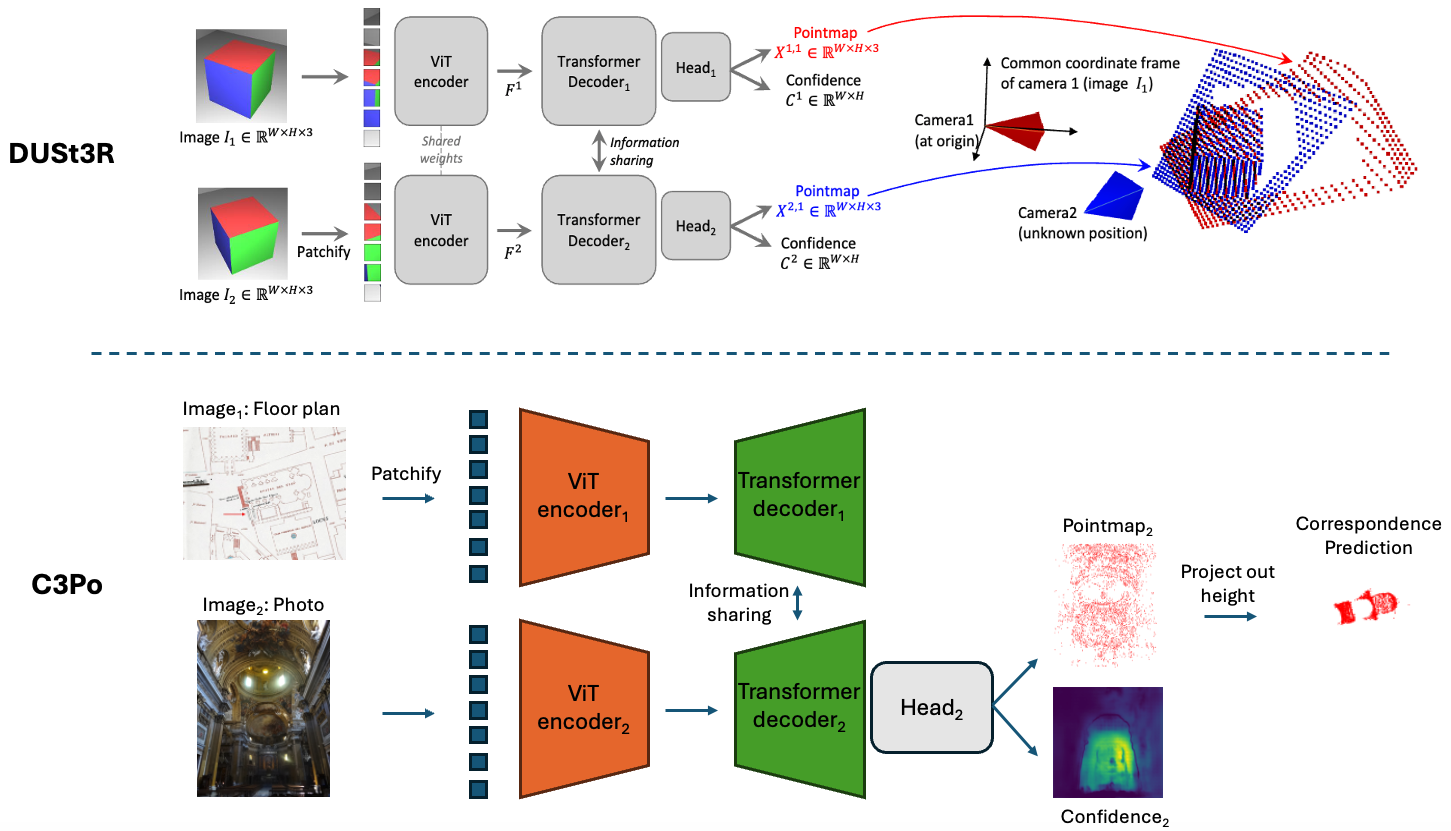
To improve performance, we pose correspondence as a pointmap prediction task and fine-tune DUSt3R for this purpose. Specifically, we set the floor plan as the reference image, which means that each image pixel can be mapped to a 3D point (x, y, z) in the floor plan coordinate frame. To obtain a correspondence, we query a photo pixel to retrieve its 3D point and project it onto the floor plan by dropping the y-coordinate — i.e. (x, y, z) → (x, z) — since the y-axis represents the vertical (up) direction in the floor plan's coordinate frame. We also experimented with discarding the z-coordinate, but this emperically led to slower model convergence. During training, we observe overfitting on the floor plans so we applied photometric augmentations (like color jittering) and geometric augmentations (like random cropping and rotation) to the floor plans to improve generalization.
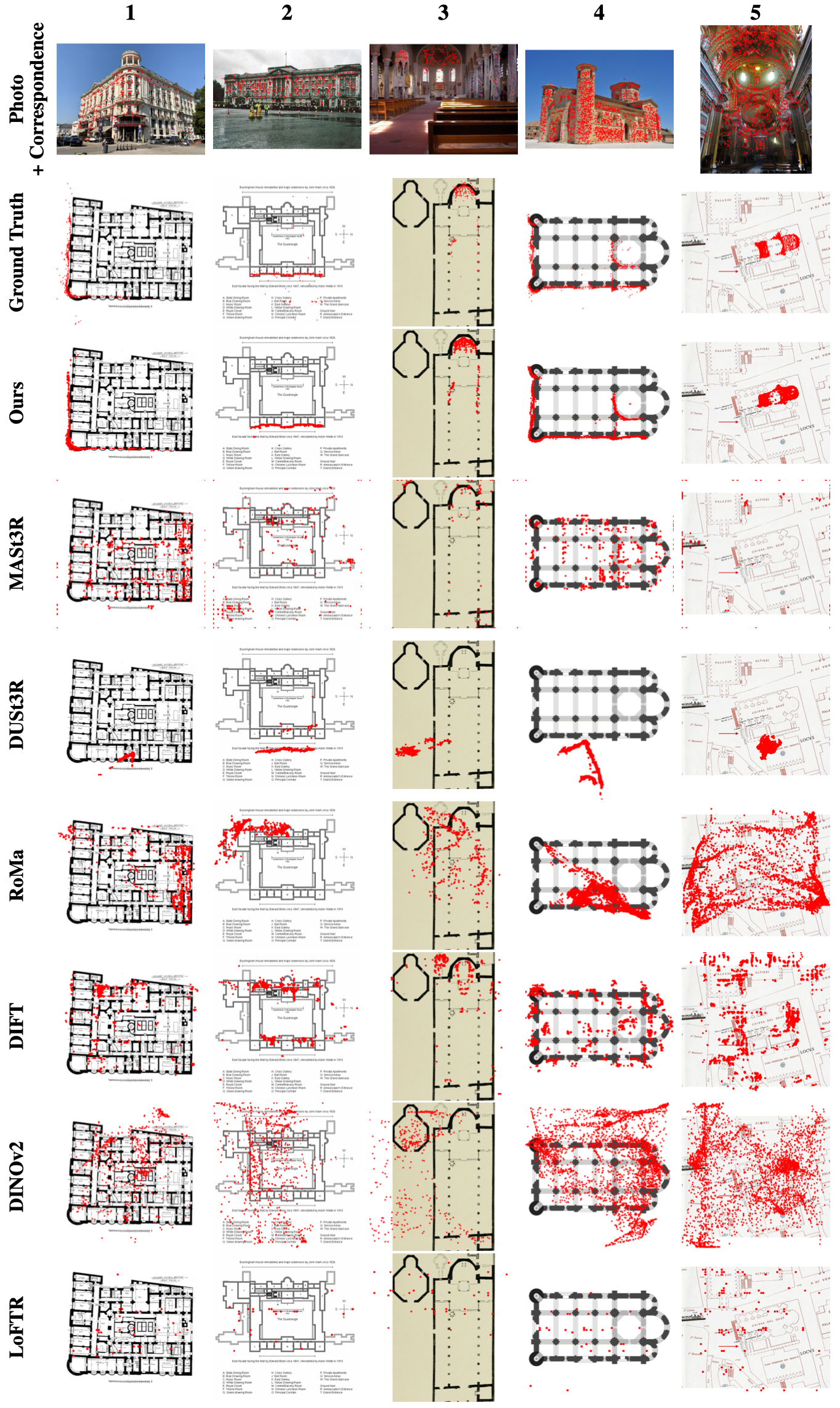
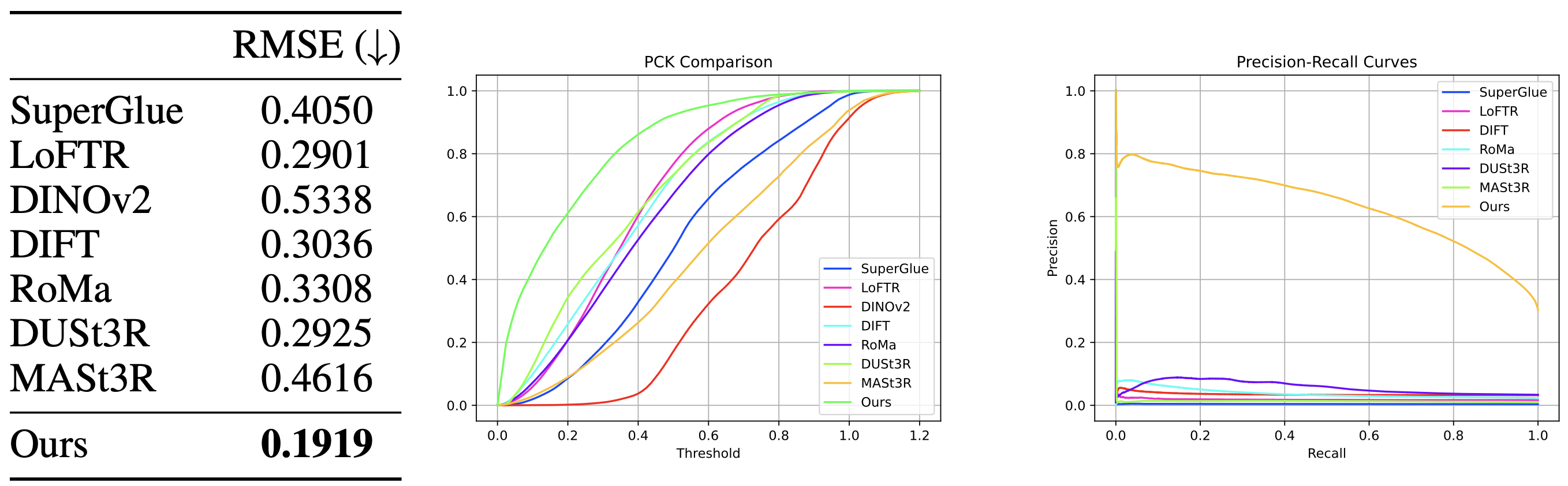
We find that correct correspondence predictions by C3Po is generally accompanied by high confidence scores, while incorrect predictions have low confidence scores. The photos from lower confidence results usually exhibit ambiguity, like the cases identified in Open Challenges, while it is more obvious to identify the camera pose of photos from the higher confidence results. This is further corroborated by the PR curves, which show that C3Po significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models because more confident correspondence predictions are more likely to be correct.
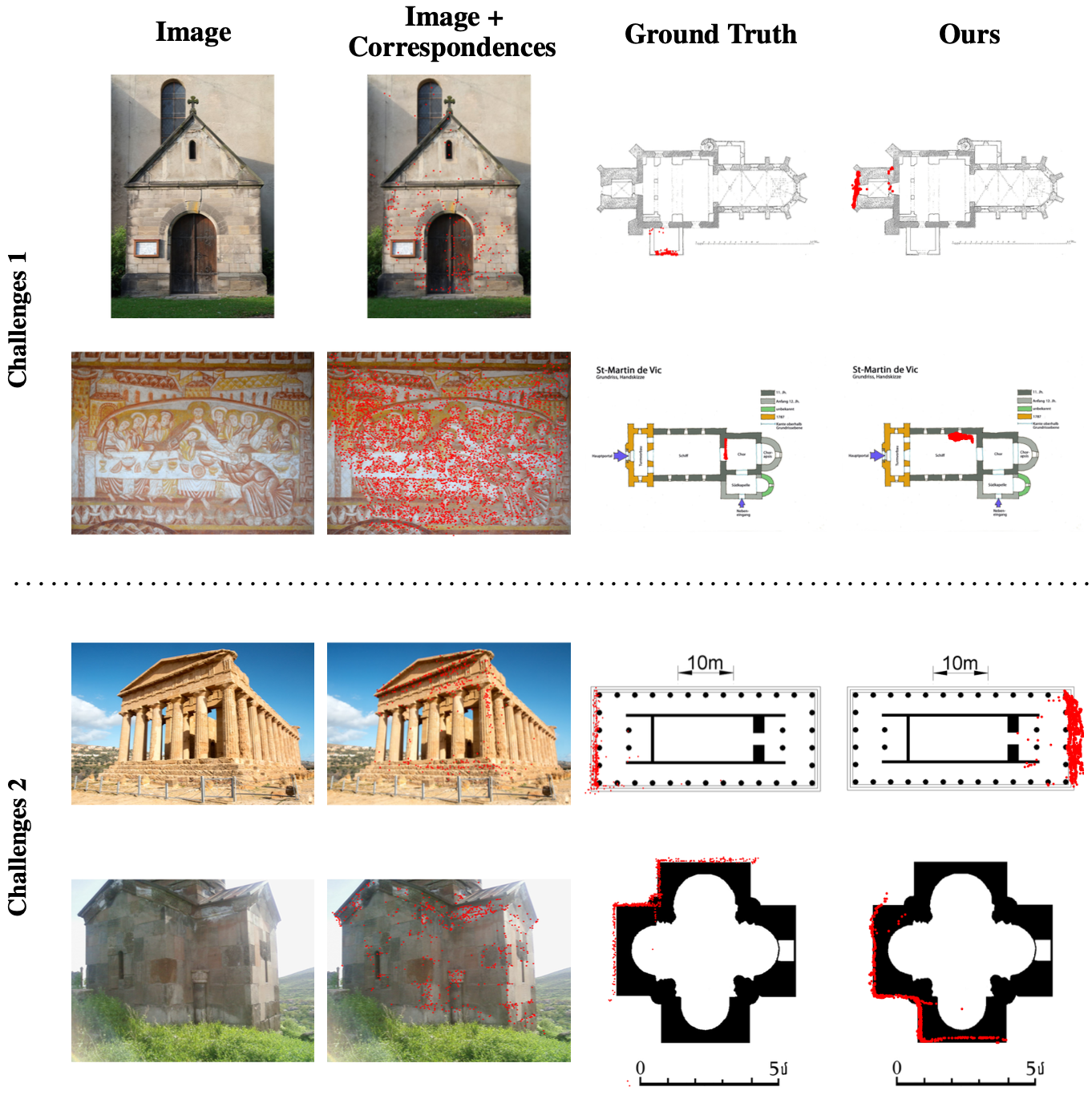
We share two categories of data that our model struggles on. Challenge 1, top two rows, are cases where the photo provides minimal context clues of where it could be on the floor plan. Challenge 2, bottom two rows, are scenes that exhibit structural symmetry, where multiple correspondence alignments would seem plausible. In all cases, our model makes plausible predictions but the answers are wrong due to lack of context or structural ambiguity.
@inproceedings{
huang2025c3po,
title={C3Po: Cross-View Cross-Modality Correspondence by Pointmap Prediction},
author={Huang, Kuan Wei and Li, Brandon and Hariharan, Bharath and Snavely, Noah},
booktitle={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={38},
year={2025}
}